Resistant Materials Coursework: Research Section Help Page
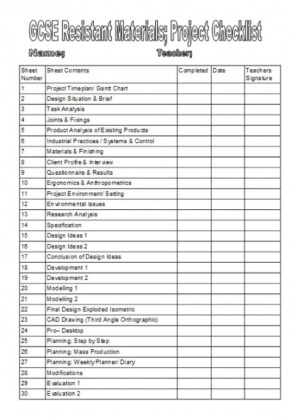
Below is a list of all the sheets you should have in your coursework folder in the Research Section. Further down the page is a detailed explanation of what should be included in each page. Where there is information to help you with that page online, I have given you links that will open in a new window.
1. Project Timeplan/ Gantt Chart
2. Design Situation & Brief
3. Task Analysis
4. Joints & Fixings
5. Product Analysis of Existing Products
6. Industrial Practices / Systems & Control
7. Materials & Finishing
8. Client Profile & Interview
9. Questionnaire & Results
10. Ergonomics & Anthropometrics
11. Project Environment/ Setting
12. Environmental Issues
13. Research Analysis
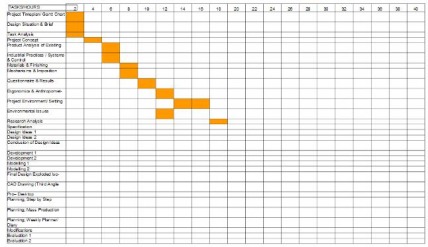
Project Timeplan/ Gantt Chart
This is a way that projects are planned over a set period of time in industry. It will gain you marks in your coursework for both the planning and industrial practices marks.
You need to use Microsoft Excel (or another spreadsheet software) to produce the plan.
Column A should contain all of the tasks that you need to complete for your coursework. You can get these tasks from your project tracking list (click below to download the sheet if you have lost yours!)
1. Project Timeplan/ Gantt Chart
2. Design Situation & Brief
3. Task Analysis
4. Joints & Fixings
5. Product Analysis of Existing Products
6. Industrial Practices / Systems & Control
7. Materials & Finishing
8. Client Profile & Interview
9. Questionnaire & Results
10. Ergonomics & Anthropometrics
11. Project Environment/ Setting
12. Environmental Issues
13. Research Analysis
Project Timeplan/ Gantt Chart
This is a way that projects are planned over a set period of time in industry. It will gain you marks in your coursework for both the planning and industrial practices marks.
You need to use Microsoft Excel (or another spreadsheet software) to produce the plan.
Column A should contain all of the tasks that you need to complete for your coursework. You can get these tasks from your project tracking list (click below to download the sheet if you have lost yours!)
Row 1 should include the hours available to you to complete the tasks. This is 40hours for your coursework. Do this in 2 hour blocks.
Think carefully about how long each task will take; remember some pages will only take 1 hour and so you will be able to fit more than 1 task into each 2 hour block.
Also remember that the development section includes your practical work, which needs to take up a lot of time as it is awarded 60% of your overall coursework marks!
Design Situation & Brief This takes up the LEFT HAND side of an A3 design sheet.
The Design Situation is a description of the problem that you are attempting to solve.
It is a paragraph of text (writing) that describes the problem. You don't say how you are going to solve the problem, only what it is.
The first sentence should explain the problem briefly. The following sentences should explain the problems in more detail.
For example;
A friend enjoys playing computer games on his Playstation 3 console and listening to music, but has a storage problem in his bedroom. The friend lives with his parents and so all of his belongings are confined to his bedroom. He often has friends round to visit and play computer games with. There is no existing storage in his bedroom for his Playstation Console & games, Ipod dock, stereo or CDs. All of his CDs and games get left on the floor and broken due to this lack of storage.
The Design Brief
This is a piece of text (writing) that explains what you are going to design and make to solve the problem.
Start the Design Brief with “I am going to design and make…” then a general description of what it is you think will solve the design problem.
Don’t be too specific! It should be flexible enough to allow your research and design work to develop over the course of the project.
Don’t be too specific when mentioning things like materials, instead state the properties the materials will need to have.
Mention points such as safety, general size, functions (what it will need to do) target market (who will buy it?).
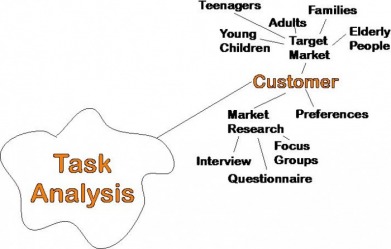
Task Analysis
This takes up the RIGHT HAND side of an A3 design sheet (the one that has your Design Brief & Situation on the left hand side!)
It is a spider diagram containing all of the areas you need to think about when designing your product.
The centre of the diagram should have the words “Task Analysis” in it. Then you will need a leg for each important area you will need to look into.
Include areas such as Aesthetics/Design, Cost, Customer/Target Market, Ergonomics, Environment, Safety, Size, Function, Materials.
Then expand each leg with detail about that area, for example;
Think carefully about how long each task will take; remember some pages will only take 1 hour and so you will be able to fit more than 1 task into each 2 hour block.
Also remember that the development section includes your practical work, which needs to take up a lot of time as it is awarded 60% of your overall coursework marks!
Design Situation & Brief This takes up the LEFT HAND side of an A3 design sheet.
The Design Situation is a description of the problem that you are attempting to solve.
It is a paragraph of text (writing) that describes the problem. You don't say how you are going to solve the problem, only what it is.
The first sentence should explain the problem briefly. The following sentences should explain the problems in more detail.
For example;
A friend enjoys playing computer games on his Playstation 3 console and listening to music, but has a storage problem in his bedroom. The friend lives with his parents and so all of his belongings are confined to his bedroom. He often has friends round to visit and play computer games with. There is no existing storage in his bedroom for his Playstation Console & games, Ipod dock, stereo or CDs. All of his CDs and games get left on the floor and broken due to this lack of storage.
The Design Brief
This is a piece of text (writing) that explains what you are going to design and make to solve the problem.
Start the Design Brief with “I am going to design and make…” then a general description of what it is you think will solve the design problem.
Don’t be too specific! It should be flexible enough to allow your research and design work to develop over the course of the project.
Don’t be too specific when mentioning things like materials, instead state the properties the materials will need to have.
Mention points such as safety, general size, functions (what it will need to do) target market (who will buy it?).
Task Analysis
This takes up the RIGHT HAND side of an A3 design sheet (the one that has your Design Brief & Situation on the left hand side!)
It is a spider diagram containing all of the areas you need to think about when designing your product.
The centre of the diagram should have the words “Task Analysis” in it. Then you will need a leg for each important area you will need to look into.
Include areas such as Aesthetics/Design, Cost, Customer/Target Market, Ergonomics, Environment, Safety, Size, Function, Materials.
Then expand each leg with detail about that area, for example;
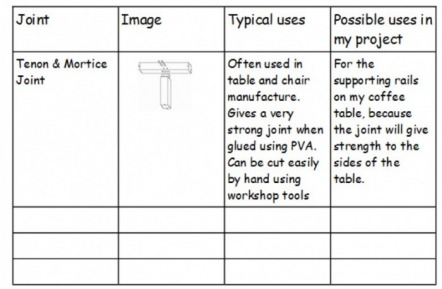
Joints & Fixings
You need to carry out research into types of wood joints and constructional fixings you could use in your project. It is best to divide the page into two, covering wood joints on one side and the other side on consructional fixings.
Either gather examples of joints and fixings from your technology room and photograph these using a digital camera, or gather research images from the internet or product catalogues. A suitable layout for the page is given below:
You need to carry out research into types of wood joints and constructional fixings you could use in your project. It is best to divide the page into two, covering wood joints on one side and the other side on consructional fixings.
Either gather examples of joints and fixings from your technology room and photograph these using a digital camera, or gather research images from the internet or product catalogues. A suitable layout for the page is given below:
Online sources of information:
Technology Student.com Scroll down a little to find the section on joints
Consructional Fixings Lots of information on constructional fixings
Technology Student.com Scroll down a little to find the section on joints
Consructional Fixings Lots of information on constructional fixings
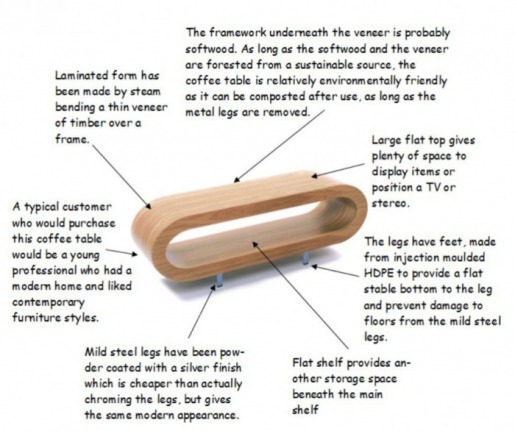
Product Analysis of Exisiting Products
You need to research what other products, similar to yours are already on the market. Find INTERESTING examples of products, that are all different to each other.
Then Analyse them, using ACCESS FM to help you. Think specifically about how the design features could help you and your own designs.
A/B grade pupils should evaluating against criteria as well as annotating the products.
You need to research what other products, similar to yours are already on the market. Find INTERESTING examples of products, that are all different to each other.
Then Analyse them, using ACCESS FM to help you. Think specifically about how the design features could help you and your own designs.
A/B grade pupils should evaluating against criteria as well as annotating the products.
Evaluating against ACCESS FM Criteria; for higher grade candidates
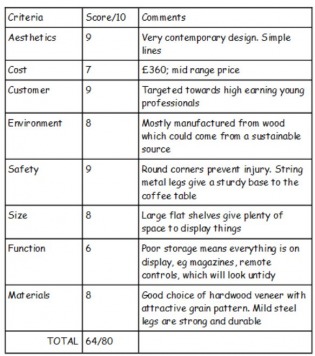
You need to complete a table to evaluate against criteria for each product. This is as well as completing the analysis through annotation shown above.
Industrial Practices This page is approached in 2 halves.
The LEFT HAND side of the page needs information on what CAD, CAM and CIM are. You need to include examples of the CAD/CAM we have in school and how these could be possibly used in your project.
CLICK HERE to visit the area of this website with information about CAD/CAM & CIM.
You also need information on scales of manufacture (one off-, Batch, Mass & JIT Production) CLICK HERE to visit a website with information about this.
The RIGHT HAND side of the page needs to cover quality control in Resistant Materials.
You need to include what is QA (Quality Assurance) & QC (Quality Control) and how is it used in mass manufacturing of products. Include information on Quality Control Checks & Tolerances.
CLICK HERE to visit a website with information about Quality Assurance.
CLICK HERE to visit a website with information about Quality Checks.
CLICK HERE to visit a website with information about Tolerances.
The LEFT HAND side of the page needs information on what CAD, CAM and CIM are. You need to include examples of the CAD/CAM we have in school and how these could be possibly used in your project.
CLICK HERE to visit the area of this website with information about CAD/CAM & CIM.
You also need information on scales of manufacture (one off-, Batch, Mass & JIT Production) CLICK HERE to visit a website with information about this.
The RIGHT HAND side of the page needs to cover quality control in Resistant Materials.
You need to include what is QA (Quality Assurance) & QC (Quality Control) and how is it used in mass manufacturing of products. Include information on Quality Control Checks & Tolerances.
CLICK HERE to visit a website with information about Quality Assurance.
CLICK HERE to visit a website with information about Quality Checks.
CLICK HERE to visit a website with information about Tolerances.
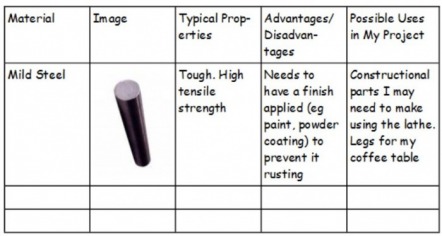
Materials & Finishing
This is split over two pages of A3. The first page is research into possible materials for your project, the second page is research into finishes you could use on your finished product.
Materials
This page needs to be laid out in the format given below. You must research three areas: Woods (Hardwoods, Softwoods, Manufactured Boards), Metals (Ferrous, Non-Ferrous, Alloys) & Plastics (Thermoplastics & Thermosetting Plastics).
As a minimum, each area must include the material name, and image, the typical properties and possible uses in your project. If you are an A/B student, you must include advantages and disadvantages of using each material, and also include some smart materials (Thermochromic pigments used in plastics/paints, smart memory alloys, polymorph)
Possible materials for research could include:
Woods
Hardwoods:Mahoghany, Beech, Balsa, Oak
Softwoods: Scots Pine, Yellow Ceder, Parahna Pine
Manufactured Boards: Hardboard, MDF, Plywood, Chip Board
Metals
Ferrous: Mild Steel, Carbon Steel, Wrought Iron
Non-Ferrous: Aluminium, Lead, Copper
Alloy: Brass, Durilium
Plastics
Thermosoftening: Acrylic, HDPE, LDPE, PVC
Thermosetting: Urea Formaldehyde, Epoxy Resin, Polyester Resin (GRP)
Smart Materials
Shape Memory Alloys
Polymorph
Thermochromic Pigments
CLICK HERE for a link to a website with information about materials
This is split over two pages of A3. The first page is research into possible materials for your project, the second page is research into finishes you could use on your finished product.
Materials
This page needs to be laid out in the format given below. You must research three areas: Woods (Hardwoods, Softwoods, Manufactured Boards), Metals (Ferrous, Non-Ferrous, Alloys) & Plastics (Thermoplastics & Thermosetting Plastics).
As a minimum, each area must include the material name, and image, the typical properties and possible uses in your project. If you are an A/B student, you must include advantages and disadvantages of using each material, and also include some smart materials (Thermochromic pigments used in plastics/paints, smart memory alloys, polymorph)
Possible materials for research could include:
Woods
Hardwoods:Mahoghany, Beech, Balsa, Oak
Softwoods: Scots Pine, Yellow Ceder, Parahna Pine
Manufactured Boards: Hardboard, MDF, Plywood, Chip Board
Metals
Ferrous: Mild Steel, Carbon Steel, Wrought Iron
Non-Ferrous: Aluminium, Lead, Copper
Alloy: Brass, Durilium
Plastics
Thermosoftening: Acrylic, HDPE, LDPE, PVC
Thermosetting: Urea Formaldehyde, Epoxy Resin, Polyester Resin (GRP)
Smart Materials
Shape Memory Alloys
Polymorph
Thermochromic Pigments
CLICK HERE for a link to a website with information about materials
Finishes
You need to research the possible finishes that can be applied to your finished product. Try to find a wide variety of possible finishes. You need to give an image and name for each type, how it is applied and the advantages & diadvantages of using each type.
CLICK HERE for information of applying finishes to wood
For metals you need to include information on Galvanising, Powder Coating, Paints, Anodising & Plating, Dip Coating
Remember plastics are self finishing and so require no additonal surface finish.
You need to research the possible finishes that can be applied to your finished product. Try to find a wide variety of possible finishes. You need to give an image and name for each type, how it is applied and the advantages & diadvantages of using each type.
CLICK HERE for information of applying finishes to wood
For metals you need to include information on Galvanising, Powder Coating, Paints, Anodising & Plating, Dip Coating
Remember plastics are self finishing and so require no additonal surface finish.
Client Profile & Interview
You need to decide who your typical customer for your product will be, and find someone who fits into this category.
Your profile needs to include information about the clients:
Age
Occupation (job)
Hobbies & Interests
Like & Dislikes
Design Preferences
Design Requirements (to have a certain function)
A photograph of the client
CLICK HERE for suggested information to gather about your client.
Questionnaire & Results You need to write a questionnaire, in leaflet format (use the templates in MS Publisher to help set up the page). The questionnaire needs to find our primary information about your chosen target market and their likes/ dislikes. Remember CLOSED questions (where the person ticks a box, gives something a rating, or rank orders things) are easier to gather reulst from than OPEN questions where they just write on a line.
You need to decide who your typical customer for your product will be, and find someone who fits into this category.
Your profile needs to include information about the clients:
Age
Occupation (job)
Hobbies & Interests
Like & Dislikes
Design Preferences
Design Requirements (to have a certain function)
A photograph of the client
CLICK HERE for suggested information to gather about your client.
Questionnaire & Results You need to write a questionnaire, in leaflet format (use the templates in MS Publisher to help set up the page). The questionnaire needs to find our primary information about your chosen target market and their likes/ dislikes. Remember CLOSED questions (where the person ticks a box, gives something a rating, or rank orders things) are easier to gather reulst from than OPEN questions where they just write on a line.
Questionnaire Results
Once you have asked a minimum of 10 people from your target market, you need to collate your results and produce some graphs. You must use MS Excel to gain the ICT marks you need.
Ergonomics & Anthropometrics
Coming soon!
Once you have asked a minimum of 10 people from your target market, you need to collate your results and produce some graphs. You must use MS Excel to gain the ICT marks you need.
Ergonomics & Anthropometrics
Coming soon!