PRINTING METHODS
These are always examined, so you need to know them all! Make sure you know the reasons WHY each one is used and what it is used to print onto.
SCREEN PRINTING
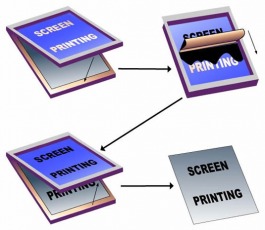
· The ink is pushed through a screen and the template of the design onto the paper below.
· Great for printing onto fabrics (bags,T- shirts) CDs, banners and even balloons.
· It is relatively cheap and stencils are made simply, often by CAM.
· Once set up, production is fast andcommercial presses can produce thousands of copies per hour.

Examples of Screen Printed Items
LETTERPRESS
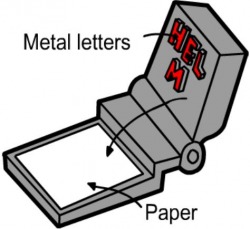
· This is the first way that things were printed and it was used extensively in the Medieval Times.
· It is basically a press, where the words to be printed are in relief (stand out) and these are inked, and pressed onto the paper. It is the basis for most modern types of relief printing.
ROTARY LETTERPRESS
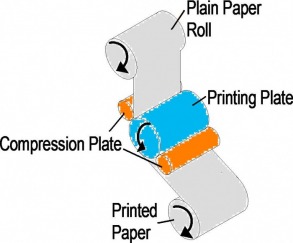
· This is a modern letterpress.
· A thin aluminium plate has the text and letters applied to it in the form of a thin sheet of rubber.
· Very ECONOMICAL for text and line work in a single colour.
· Usually used for books and wallpaper. Not good for fine detail and photographs. Is occasionally used for basic packaging.

Examples of Rotary Letterpress Items
FLEXOGRAPHY
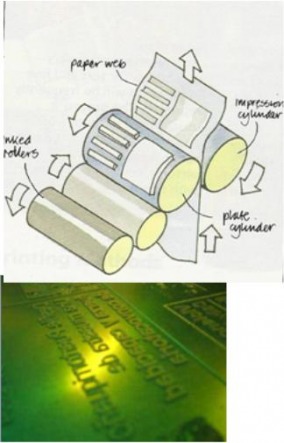
• Flexography is a similar process to the letterpress.
• A thin ALUMINIUM plate has the text and letters applied to it in the form of a thin sheet of rubber, using a photographic technique. The printing areas are RAISED.
• It is used for printing NON PAPER ITEMS, eg Polythene food packaging and corrugated card Point of Sale stands, sticky labels and carrier bags.
• It DRIES QUICKLY as the carrier in the ink evaporates quickly, allowing further die cutting and packing to happen immediately.

Examples of Flexography Printed Items
LITHOGRAPHY
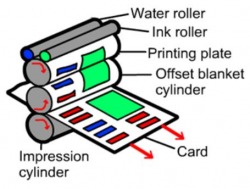
· Lithography is the most commonly used printing process and is used to print THOUSANDS of copies of the same item, in one production run.
· Lithography machines can print on BOTH sides of paper.
· The images is transferred onto the FLAT printing plate photographically using UV light
· The plate is washed in a chemical that makes the image area attract the oil based ink. The non-image is kept wet with water and repels the ink
· It is only used for medium to large print (250,000 - million item) runs because the set up costs are EXPENSIVE
· It is used for orders of many hundered of thousands of leaflets, posters and newspapers, letterheads and packaging.

Examples of Lithographic Printed Items
GRAVURE
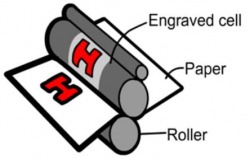
· Gravure is used to produce HIGH QUALITY photographic images.
· It is very EXPENSIVE due to the skill needed to manufacture the printing plate.
· It is the opposite to letterpress – the printing areas are in fact LOWER then the non-printing areas. The image is ENGRAVED onto a COPPER PLATE, creating cells that are filled with a spirit based ink. The paper is pressed against these cells to produce the image. The ink evaporates quickly once printed.
· Gravure is used for very BIG PRINT RUNS of glossy magazines, mail order catalogues and weekend newspaper supplements that contain lots of images. It is also used to reproduce artwork as prints and stamps.

Examples of Gravure Printed Items
CHOOSING THE CORRECT PRINTING METHOD; THE PROS & CONS

